seaborn.JointGrid(**kwargs)¶Grid for drawing a bivariate plot with marginal univariate plots.
Many plots can be drawn by using the figure-level interface jointplot().
Use this class directly when you need more flexibility.
__init__(self, *, x=None, y=None, data=None, height=6, ratio=5, space=0.2, dropna=False, xlim=None, ylim=None, size=None, marginal_ticks=False, hue=None, palette=None, hue_order=None, hue_norm=None)¶Set up the grid of subplots and store data internally for easy plotting.
dataVariables that specify positions on the x and y axes.
pandas.DataFrame, numpy.ndarray, mapping, or sequenceInput data structure. Either a long-form collection of vectors that can be assigned to named variables or a wide-form dataset that will be internally reshaped.
Size of each side of the figure in inches (it will be square).
Ratio of joint axes height to marginal axes height.
Space between the joint and marginal axes
If True, remove missing observations before plotting.
Set axis limits to these values before plotting.
If False, suppress ticks on the count/density axis of the marginal plots.
dataSemantic variable that is mapped to determine the color of plot elements.
Note: unlike in FacetGrid or PairGrid, the axes-level
functions must support hue to use it in JointGrid.
matplotlib.colors.ColormapMethod for choosing the colors to use when mapping the hue semantic.
String values are passed to color_palette(). List or dict values
imply categorical mapping, while a colormap object implies numeric mapping.
Specify the order of processing and plotting for categorical levels of the
hue semantic.
matplotlib.colors.NormalizeEither a pair of values that set the normalization range in data units or an object that will map from data units into a [0, 1] interval. Usage implies numeric mapping.
See also
Examples
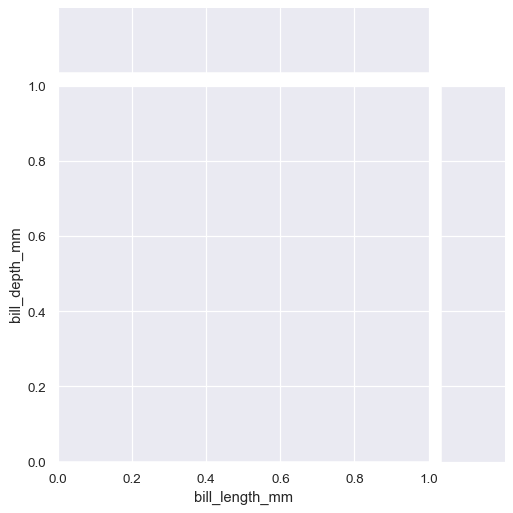
Calling the constructor initializes the figure, but it does not plot anything:
penguins = sns.load_dataset("penguins")
sns.JointGrid(data=penguins, x="bill_length_mm", y="bill_depth_mm")
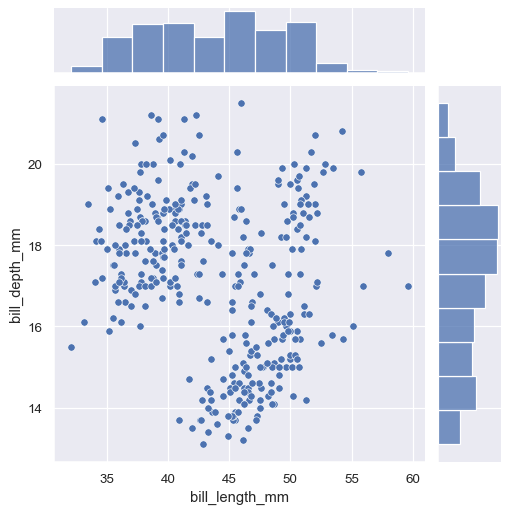
The simplest plotting method, JointGrid.plot() accepts a pair of functions (one for the joint axes and one for both marginal axes):
g = sns.JointGrid(data=penguins, x="bill_length_mm", y="bill_depth_mm")
g.plot(sns.scatterplot, sns.histplot)
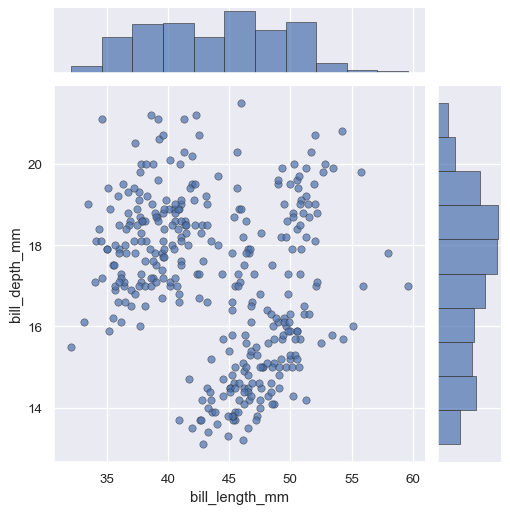
The JointGrid.plot() function also accepts additional keyword arguments, but it passes them to both functions:
g = sns.JointGrid(data=penguins, x="bill_length_mm", y="bill_depth_mm")
g.plot(sns.scatterplot, sns.histplot, alpha=.7, edgecolor=".2", linewidth=.5)
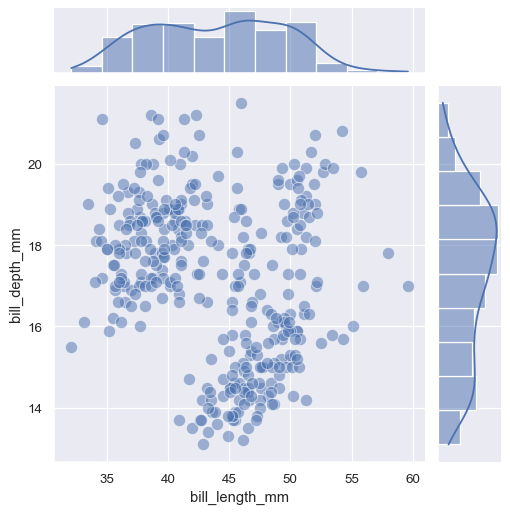
If you need to pass different keyword arguments to each function, you’ll have to invoke JointGrid.plot_joint() and JointGrid.plot_marginals():
g = sns.JointGrid(data=penguins, x="bill_length_mm", y="bill_depth_mm")
g.plot_joint(sns.scatterplot, s=100, alpha=.5)
g.plot_marginals(sns.histplot, kde=True)
You can also set up the grid without assigning any data:
g = sns.JointGrid()
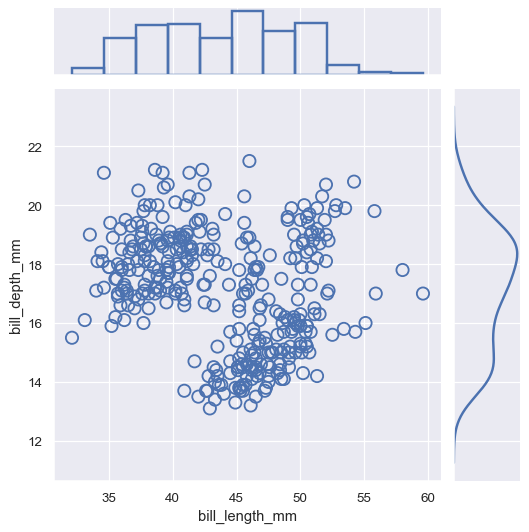
You can then plot by accessing the ax_joint, ax_marg_x, and ax_marg_y attributes, which are matplotlib.axes.Axes objects:
g = sns.JointGrid()
x, y = penguins["bill_length_mm"], penguins["bill_depth_mm"]
sns.scatterplot(x=x, y=y, ec="b", fc="none", s=100, linewidth=1.5, ax=g.ax_joint)
sns.histplot(x=x, fill=False, linewidth=2, ax=g.ax_marg_x)
sns.kdeplot(y=y, linewidth=2, ax=g.ax_marg_y)
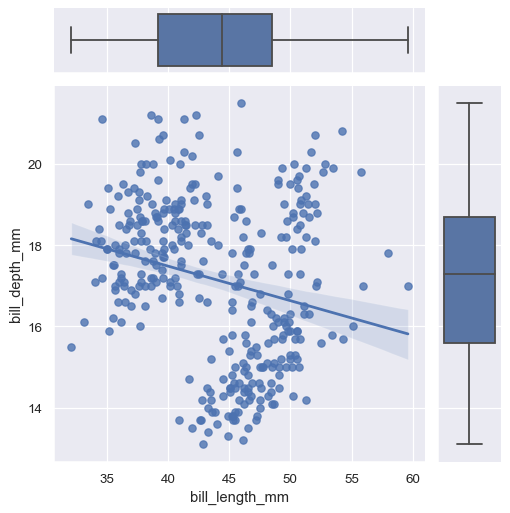
The plotting methods can use any seaborn functions that accept x and y variables:
g = sns.JointGrid(data=penguins, x="bill_length_mm", y="bill_depth_mm")
g.plot(sns.regplot, sns.boxplot)
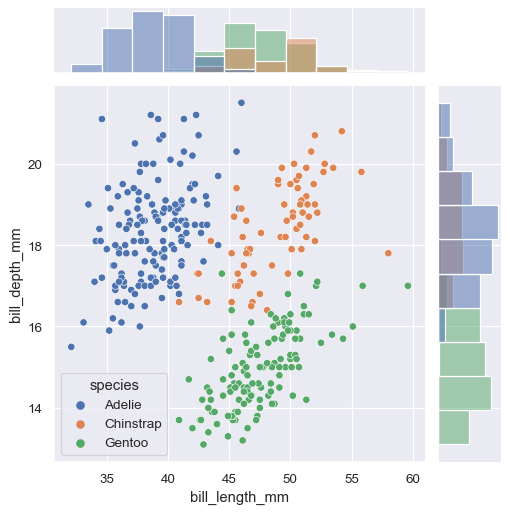
If the functions accept a hue variable, you can use it by assigning hue when you call the constructor:
g = sns.JointGrid(data=penguins, x="bill_length_mm", y="bill_depth_mm", hue="species")
g.plot(sns.scatterplot, sns.histplot)
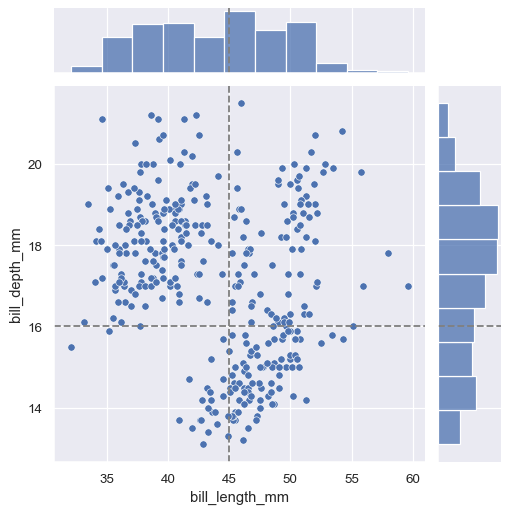
Horizontal and/or vertical reference lines can be added to the joint
and/or marginal axes using :meth:JointGrid.refline:
g = sns.JointGrid(data=penguins, x="bill_length_mm", y="bill_depth_mm")
g.plot(sns.scatterplot, sns.histplot)
g.refline(x=45, y=16)
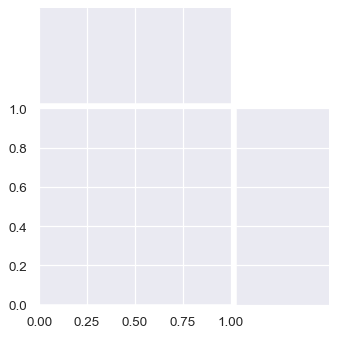
The figure will always be square (unless you resize it at the matplotlib layer), but its overall size and layout are configurable. The size is controlled by the height parameter. The relative ratio between the joint and marginal axes is controlled by ratio, and the amount of space between the plots is controlled by space:
sns.JointGrid(height=4, ratio=2, space=.05)
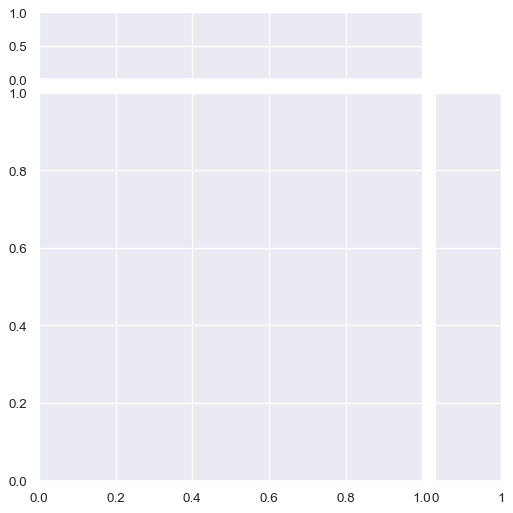
By default, the ticks on the density axis of the marginal plots are turned off, but this is configurable:
sns.JointGrid(marginal_ticks=True)
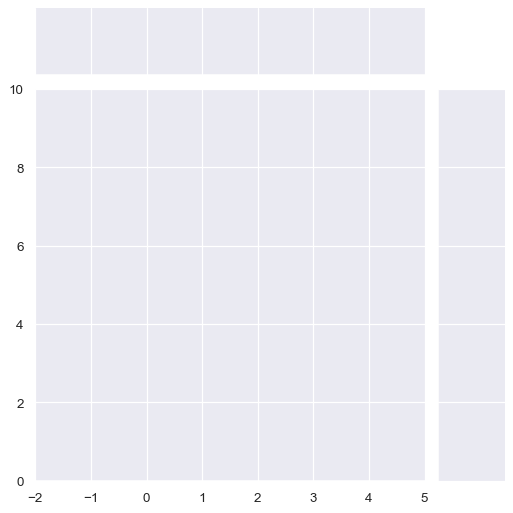
Limits on the two data axes (which are shared across plots) can also be defined when setting up the figure:
sns.JointGrid(xlim=(-2, 5), ylim=(0, 10))
Methods
|
Set up the grid of subplots and store data internally for easy plotting. |
|
Draw the plot by passing functions for joint and marginal axes. |
|
Draw a bivariate plot on the joint axes of the grid. |
|
Draw univariate plots on each marginal axes. |
|
Add a reference line(s) to joint and/or marginal axes. |
|
Save an image of the plot. |
|
Set attributes on each subplot Axes. |
|
Set axis labels on the bivariate axes. |
Attributes
|
DEPRECATED: prefer the |
|
Access the |